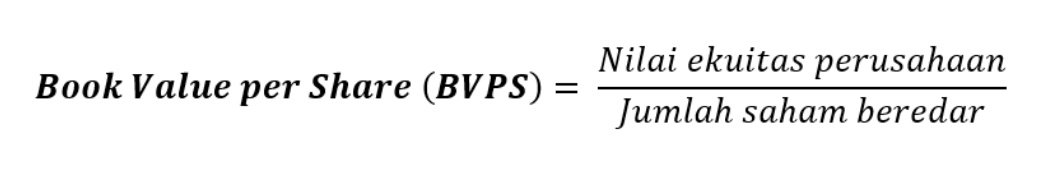
By repurchasing 1,000,000 common shares from the company’s shareholders, the BVPS increased from $3.00 to $4.50. BVPS is typically calculated and published periodically, xero community such as quarterly or annually. This infrequency means that BVPS may not always reflect the most up-to-date value of a company’s assets and liabilities.
How often is BVPS calculated?
This means that each share of the company would be worth $8 if the company got liquidated. Now, let’s say that you’re considering investing in either Company A or Company B. Given that Company B has a higher book value per share, you might find it tempting to invest in that company. However, you would need to do some more research before making a final decision. It’s easy to get started when you open an investment account with SoFi Invest. You can invest in stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, and more. SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here).
- Total liabilities include items like debt obligations, accounts payable, and deferred taxes.
- The price per book value is a way of measuring the value offered by a firm’s shares.
- In contrast, video game companies, fashion designers, or trading firms may have little or no book value because they are only as good as the people who work there.
- If the company has been depreciating its assets, investors might need several years of financial statements to understand its impact.
- The relationship between the two quantifies the premium that investors are paying (or not) to own that stock.
- Amanda Bellucco-Chatham is an editor, writer, and fact-checker with years of experience researching personal finance topics.
Repurchase Common Stocks
Book valuation might be too high if the company is a bankruptcy candidate and has liens against its assets. What is more, assets will not fetch their full values if creditors sell them in a depressed market at fire-sale prices. Mathematically, book value is the difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities. An even better approach is to assess a company’s tangible book value per share (TBVPS).
What Is Price Per Book Value?
Both valuations can be helpful in calculating whether a stock is fairly valued, overvalued, or undervalued. In this article, we’ll delve into the differences between the two and how they are used by investors and analysts. Creditors who provide the necessary capital to the business are more interested in the company’s asset value. Therefore, creditors use book value to determine how much capital to lend to the company since assets make good collateral.

For example, a company can use profits to either purchase more company assets, pay off debts, or both. These methods would increase the common equity available to shareholders, and hence, raise the BVPS. Whereas some price models and fundamental analyses are complex, calculating book value per share is fairly straightforward.
BVPS is significant for investors because it offers a snapshot of a company’s net asset value per share. By analyzing BVPS, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, aiding in the assessment of whether a stock is over or undervalued. This formula shows the net asset value available to common shareholders, excluding any preferred equity. Taking this idea forward, investors will often look at a company’s book value per share or BVPS. Annual additions to accumulated depreciation are intended to reflect an asset’s loss of value over time. But these are formulaic accounting entries — such that an asset’s book value doesn’t necessarily align with its market value.
He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. For example, during the Great Recession, Bank of America’s market value was below its book value. As of 2024, the company’s market value is no longer trading at a discount to its book value.
Book Value per Share (BVPS) is the ratio of a company’s equity available to common shareholders to the number of outstanding company shares. This ratio calculates the minimum value of a company’s equity and determines a firm’s book value, or Net Asset Value (NAV), on a per-share basis. In other words, it defines the accounting value (i.e. book value) of a share of a company’s publicly-traded stock. Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company. The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market. Total assets cover all types of financial assets, including cash, short-term investments, and accounts receivable.
The figure of 1.25 indicates that the market has priced shares at a premium to the book value of a share. The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently. There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company.
